‘Hangxiety’: why alcohol gives you a hangover and anxiety
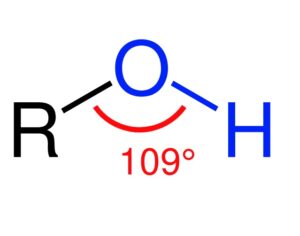
Alcohol, he says, targets the Gaba (gamma-aminobutyric acid) receptor, which sends chemical messages through the brain and central nervous system to inhibit the activity of nerve cells. Put simply, it calms the brain, reducing excitement by making fewer neurons fire. “Alcohol stimulates Gaba, which is why you get relaxed and cheerful when you drink,” explains Nutt.
The first two drinks lull you into a blissful Gaba-induced state of chill. When you get to the third or fourth drink, another brain-slackening effect kicks in: you start blocking glutamate, the main excitatory transmitter in the brain. “More glutamate means more anxiety,” says Nutt. “Less glutamate means less anxiety.” This is why, he says, “when people get very drunk, they’re even less anxious than when they’re a bit drunk” – not only does alcohol reduce the chatter in your brain by stimulating Gaba, but it further reduces your anxiety by blocking glutamate. In your blissed-out state, you will probably feel that this is all good – but you will be wrong. The body registers this new imbalance in brain chemicals and attempts to put things right. It is a little like when you eat a lot of sweets and your body goes into insulin-producing overdrive to get the blood sugar levels down to normal; as soon as the sweets have been digested, all that insulin causes your blood sugar to crash. When you are drunk, your body goes on a mission to bring Gaba levels down to normal and turn glutamate back up. When you stop drinking, therefore, you end up with unnaturally low Gaba function and a spike in glutamate – a situation that leads to anxiety, says Nutt. “It leads to seizures as well, which is why people have fits in withdrawal.”
Original Article (The Guardian):
‘Hangxiety’: why alcohol gives you a hangover and anxiety
Artwork Fair Use: Willem van de Pol