The current state of research on ayahuasca
A systematic review of human studies assessing psychiatric symptoms, neuropsychological functioning, and neuroimaging.
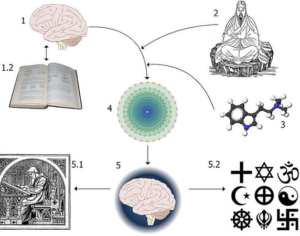
Acute AYA administration was well tolerated, increased introspection and positive mood, altered visual perceptions, activated frontal and paralimbic regions and decreased default mode network activity. It also improved planning and inhibitory control and impaired working memory, and showed anti-depressive and anti-addictive potentials. Long-term AYA use was associated with increased cortical thickness of the anterior cingulate cortex and cortical thinning of the posterior cingulate cortex, which was inversely correlated to age of onset, intensity of prior AYA use, and spirituality. Subacute and long-term AYA use was not associated with increased psychopathology or cognitive deficits, being associated with enhanced mood and cognition, increased spirituality, and reduced impulsivity.
Original Article (Journal of Psychopharmacology):
The current state of reseach on ayahhuasca: A systematic review of human studies assessing psychiatric symptoms, neuropsychological functioning, and neuroimaging
Artwork Fair Use: CostaPPPR