What is iboga and can it actually cure opioid addiction?
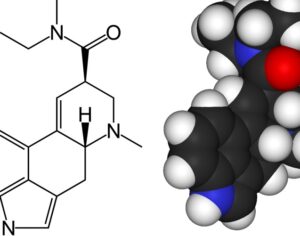
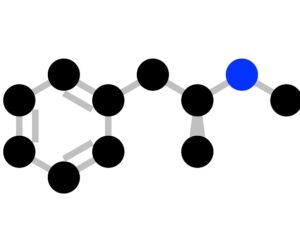
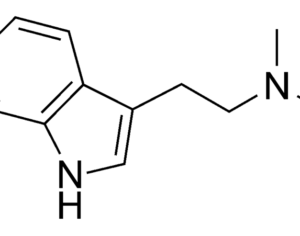
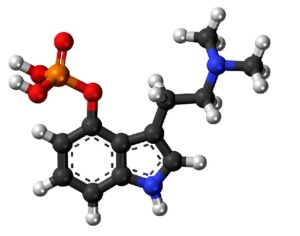
Ibogaine (12-methoxyibogamine) is the main alkaloid of at least 12 alkaloids found in the Tabernanthe iboga plant.
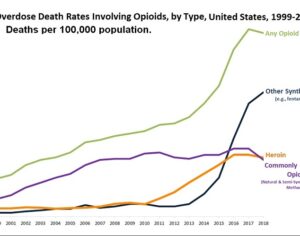
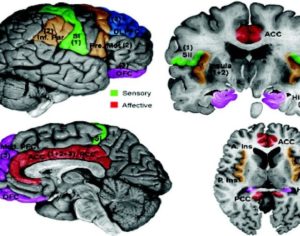
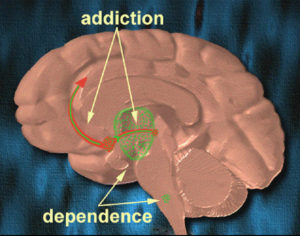
[One of the alkaloids, mentioned above] seems to activate the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) pathway in the ventral tegmental area of the brain, increasing its expression. Previous studies have found that the GDNF pathway plays a unique role in mitigating the negative effects of drugs with a high potential for abuse and raises the survivability of adult dopamine-related neurons. The synaptic remodeling may change the responsiveness of the mesolimbic dopaminergic system, thereby canceling the ‘rewarding effect’ and neuroadaptations induced by drug abuse. Such ibogaine-induced changes in GDNF expression may serve to explain the psychedelic drug’s potential efficacy against serious drug addiction … Animal studies suggest that within 24 hours after ingesting ibogaine, the alkaloids produce significant attenuation of opioid withdrawal signs in different animal species. What’s more, the substance also reduces the self-administration of other potent drugs such as cocaine, amphetamine, methamphetamine, alcohol, and nicotine. In one study performed on humans, involving 33 participants with opioid dependence, withdrawal signs were completely resolved in 29 of the participants (88%). This was not a controlled clinical trial, however.
From the Article (ZME Science):
What is iboga and can it actually cure opioid addiction?
Artwork Fair Use: Alvesgaspar