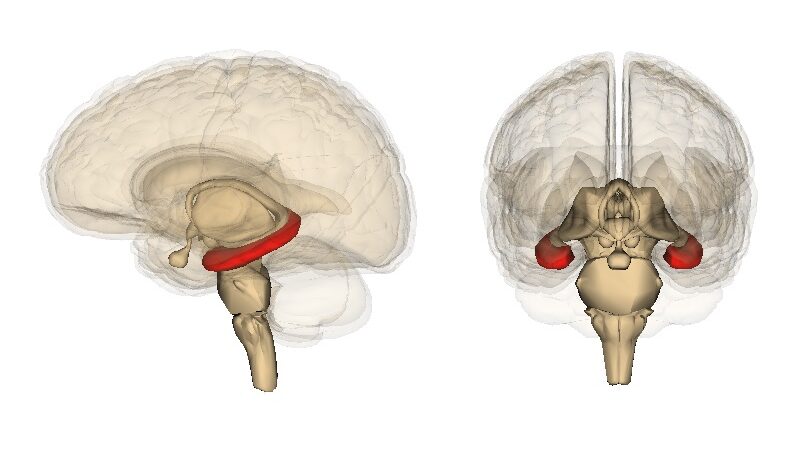
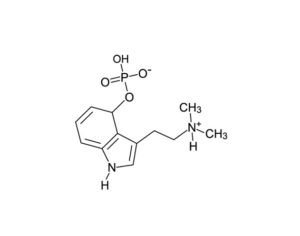
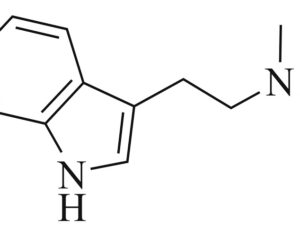
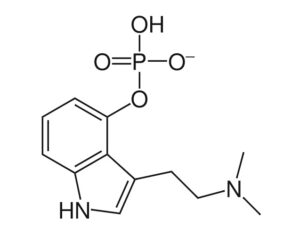
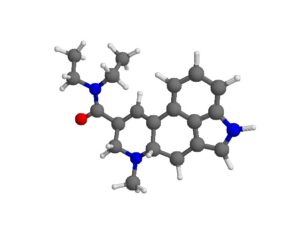
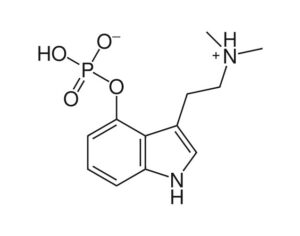
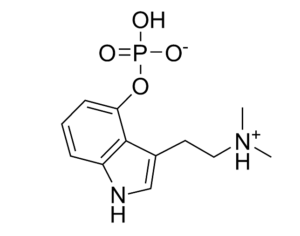
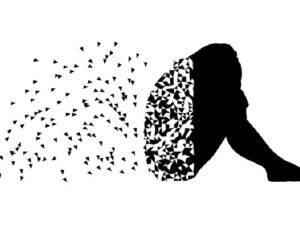
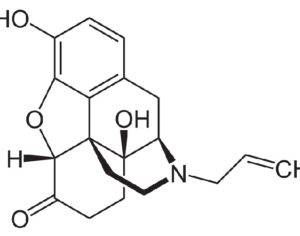
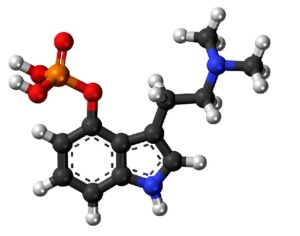
Can psilocybin stimulate neurogenesis in the hippocampus?
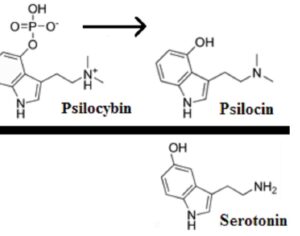
Increasing evidence suggests psilocybin may promote neuroplasticity, contributing to its antidepressant effects.
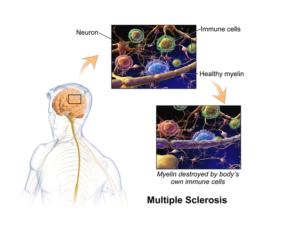
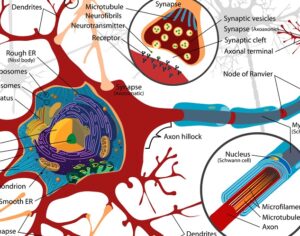
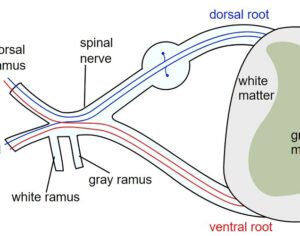
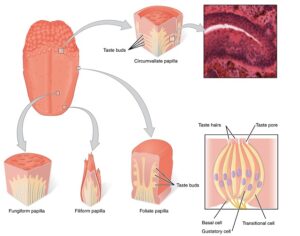
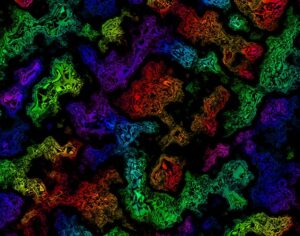
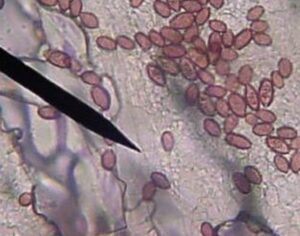
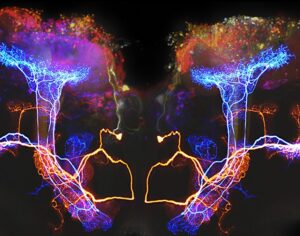
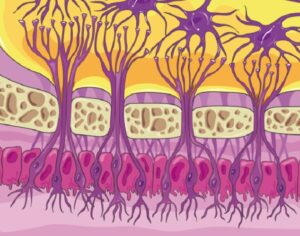
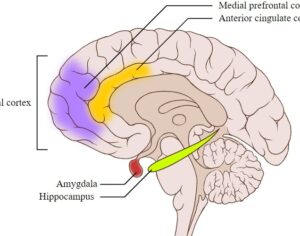
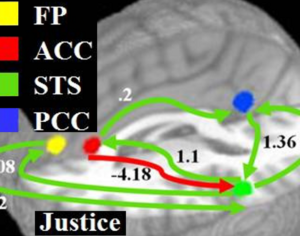
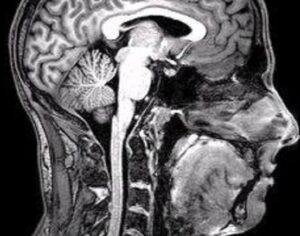
In some people, postmortem studies indicate, depression may be related to disrupted adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN)—the birth and growth of new neurons in the hippocampus. This mechanism is important for regulating mood and maintaining spatial learning and memory throughout life, and it is critical for brain plasticity… in mice… the fear response of mice improved, and the effect was associated with several indicators of increased hippocampal neurogenesis. Psilocybin increased the number and density of dendritic branches and synaptic connections in the hippocampus; likely related to increased levels of BDNF, which supports proliferation and differentiation of hippocampal progenitor cells. One week after the fear-conditioned mice received psilocybin, the researchers found a higher number of cells labelled with BrdU and doublecortin (DCX), a marker of proliferating cells and immature neurons, respectively, in the dentate gyrus.
Original Article (Psychology Today):
Can psilocybin stimulate neurogenesis in the hippocampus?
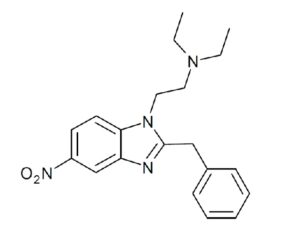
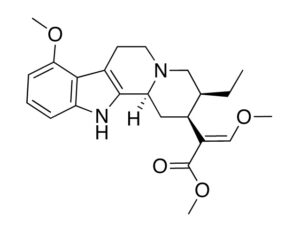
Artwork Fair Use: Life Science Databases


























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Recent Comments