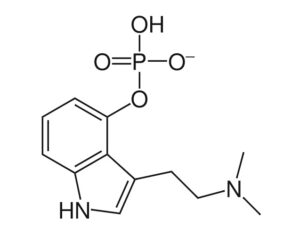
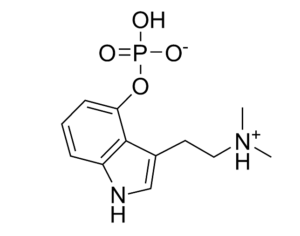
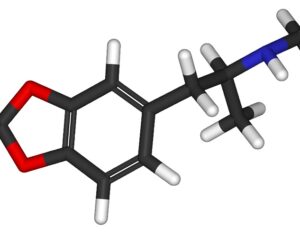
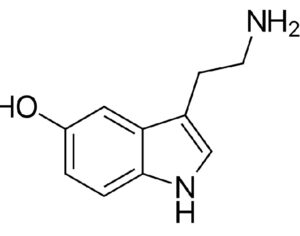
Psilocybin induces acute and persisting alterations in immune status and the stress response in healthy volunteers
Patients characterized by stress-related disorders such as depression display elevated circulating concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines and a hyperactive HPA axis. Psychedelics are demonstrating promising results in treatment of such disorders…
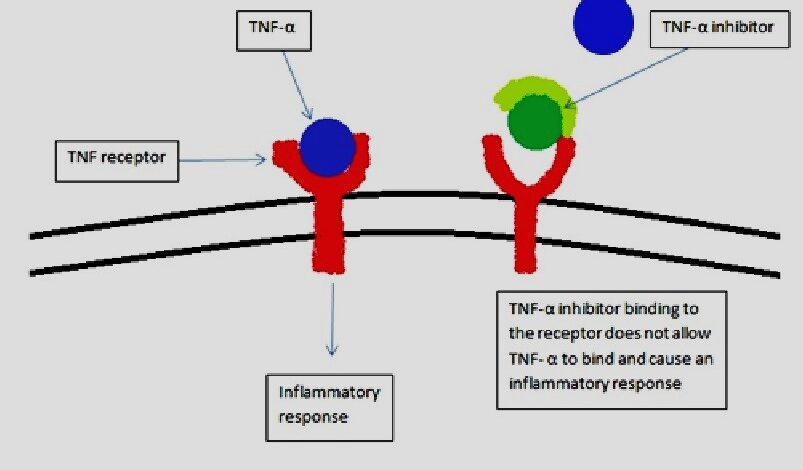
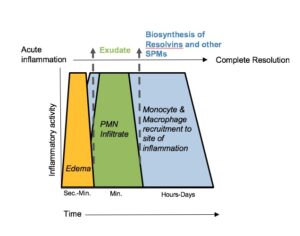
Psilocybin immediately reduced concentrations of the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), while other inflammatory markers (interleukin (IL)-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, and C-reactive protein (CRP)) remained unchanged. Seven days later, TNF-α concentrations returned to baseline, while IL-6 and CRP concentrations were persistently reduced in the psilocybin group.
Original Article (Medrxiv, British Medical Journal, Yale, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory):
Psilocybin induces acute and persisting alterations in immune status and the stress response in healthy volunteers
Artwork Fair Use: I4mc4lvin



















































































































































































































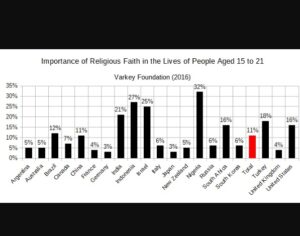











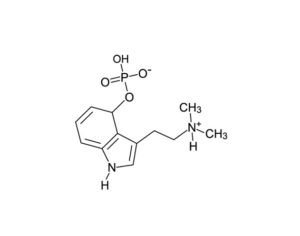
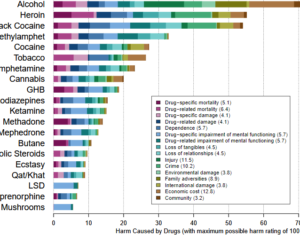

































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































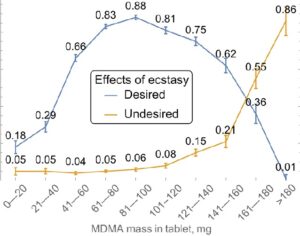

































































































































































Recent Comments